- Enter appropriate numbers in the boxes,
- enter your email address,
- click on submit, and
- wait for results to be returned to your email.
(this will take about 15 minutes)
http://www.jwave.vt.edu/output/wave2d_30x60_ "unique date-time"/. If your email does not provide direct web links, copy and paste the web address from the email into your web browser location window.
http://www.jwave.rkriz.net/output/wave2d_30x60_"unique date-time" /results.html
If the form is submitted "as-is" you can view the simulation results as an animation.
Here are some images with
back-ground-info that describes this problem in more detail.
=====================================================
ANIMATION: ( MPEG(768K) )
How to Visually Interpret Results
============================================================
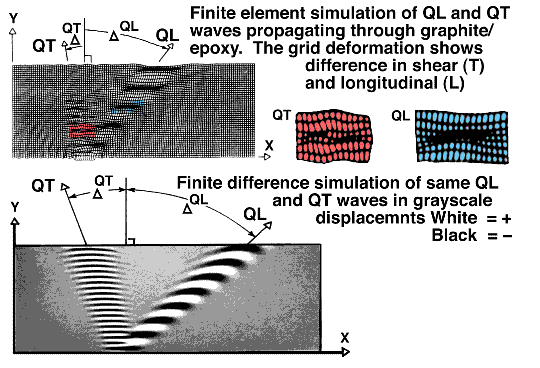
BULK WAVE PROPAGATION SIMULATION IN UNIDIRECTIONAL Gr/Ep
-----------------------------------------------------------
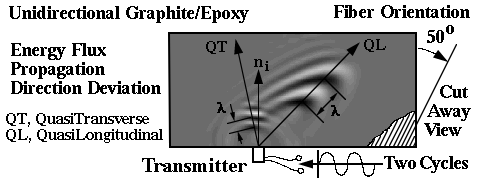
Unlike isotropic materials waves propating in anisortropic materials deviate from
the wave normal ni. This anisotropy quides the wave energy propagation shown in
the animations provided above. From this simulation new relationships can be
seen: 1) the faster moving QL wave has a longer wavelength, 2) diffractions
from reflected bulk waves create Rayleigh surface waves, 3) the reflected QL
wave energy propagates back towards the origin, 4) this refection does not
generate another bifrucation of energy into yet another QL & QT wave. This
information suggested that waves could be launched preferentially